반응형

Map<K, V> Interface
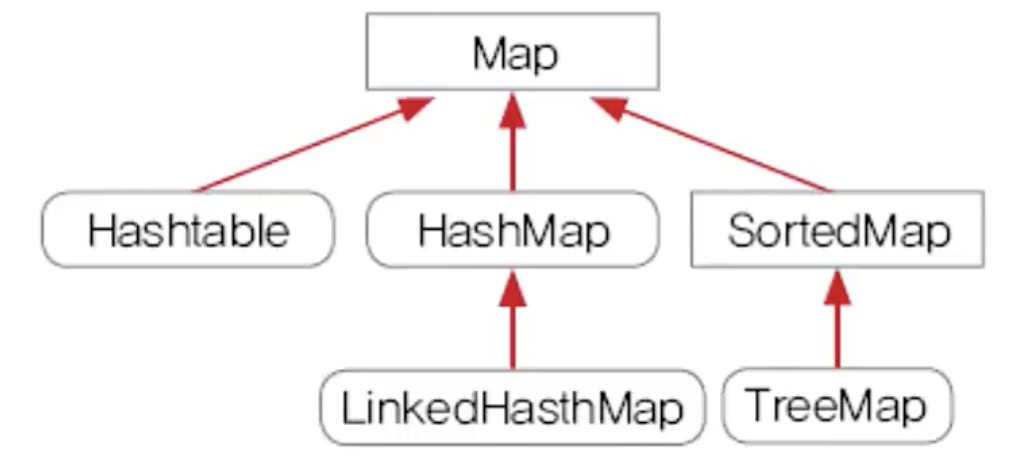
- Map<K, V> Interface
- K : Key, data의 식별자
- V : Value, 실제 data
- 즉 Key - Value의 쌍으로 data를 유지하기 위한 Interface
- iterable을 상속하지 않음.
- Iterator를 사용하지 못함
▶ HashMap<K, V>
- Map Interface를 구현한 대표적인 Collection Class
- Hash Algorithm 기반의 분류기능을 가진 Map구조.
- 분류
Unique : 보안에서 사용
▶ LinkedHashMap
- 순서가 있다.
▶ TreeMap <K, V>
- 범위 검색, 정렬에 유리한 Colleciton class
- 이진탐색트리 구조
- HashMap보다 데이터 추가, 삭제에 시간이 더 걸림
▶ 메서드
| 메서드 | 설명 |
| void clear() | Map의 모든 객체를 삭제한다. |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | 지정된 key객체와 일치하는 Map의 key객체가 있는지 확인한다. |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | 지정된 value객체와 일치하는 Map의 Value객체가 있는지 확인한다. |
| Set entrySet() | Map에 저장되어 있는 key-value쌍을 Map.Entry 타입의 객체로 저장한 set으로 반환한다. |
| boolean equals(Object o) | 동일한 Map인지 비교한다. |
| Object get(Object key) | 지정한 key객체에 대응하는 value객체를 찾아서 반환한다. |
| int hashCode() | 해시코드를 반환한다. |
| boolean isEmpty() | Map이 비어 있는지 확인한다. |
| Set keySet() | Map에 저장된 모든 key객체를 반환한다. |
| Object put(Object key, Object Value) | Map에 value객체를 key객체에 연결(mapping)하여 저장한다. |
| void putAll(Map t) | 지정된 Map의 모든 key-value쌍을 추가한다. |
| Object remove(Object key) | 지정한 key객체와 일치하는 key-value객체를 삭제한다. |
| int size() | Map에 저장된 key-value쌍의 개수를 반환한다. |
| Collection values() | Map에 저장된 모든 value 객체를 반환한다. |
HashMap
- Hashing(해싱) 기법으로 데이터를 저장.
- 데이터가 많아도 검색이 빠르다.
- Map Interface를 구현.
- 데이터를 key, value의 쌍으로 저장.
| key | Collection내의 key중에서 유일해야한다. |
| value | key와 달리 데이터의 중복을 허용한다. |
▶ Hashing
hash function로 hash table에 데이터를 저장하고 검색한다.
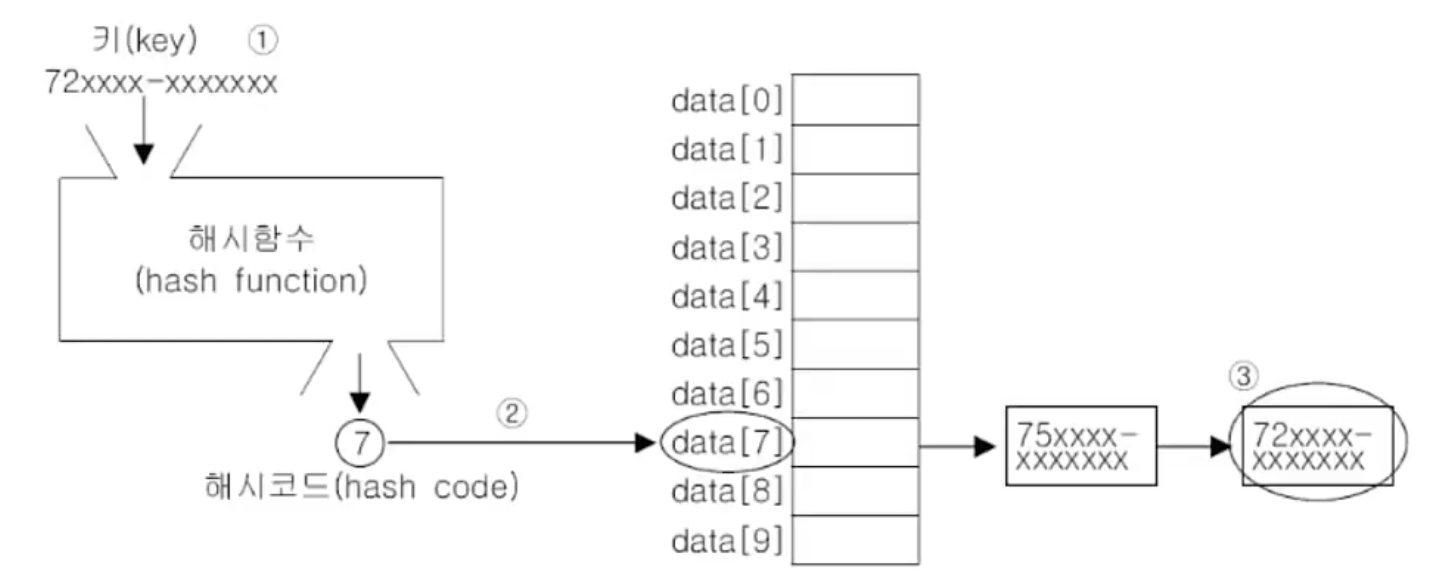
- 키로 해시함수를 호출해서 해시코드를 얻는다.
- 해시코드(해시함수의 반환값)에 대응하는 링크드리스트를 배열에서 찾는다.
- 링크드리스트에서 키와 일치하는 데이터를 찾는다.
※ 해시함수는 같은 키에 대해 항상 같은 해시코드를 반환해야한다. 서로 다른 키일지라도 같은 값의 해시코드를 반환 할 수 도 있다.
* hash table은 배열과 linked list가 조합된 상태
- 접근성, 변경이 유리
▶ 메서드
| 생성자 / 메서드 | 설명 |
| HashMap() | HashMap() 객체를 생성 |
| HashMap(int initialCapacity) | 지정된 값을 초기용량으로 하는 HashMap객체를 생성 |
| HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) | 지정된 Map의 모든 요소를 포함하는 HashMap을 생성 |
| HashMap(Map m) | 지정된 Map의 모든 요소를 포함하는 HashMap을 생성 |
| void clear() | HashMap에 저장된 모든 객체를 제거 |
| Object clone() | 현재 HashMap을 복제해서 반환 |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | HashMap에 지정된 키가 포함되어 있는지 알려준다. (포함되어 있으면 true) |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | HashMap에 지정된 값(value)가 포함되어 있는지 알려준다. |
| Set entrySet() | HashMap에 저장된 키와 값을 엔트리(키와 값의 결합)의 형태로 Set에 저장해서 반환 |
| Object get(Object key) | 지정된 key의 값을 반환, 못찾으면 null 반환 |
| Object getOrDefault(Object key, Object defaultValue) | 지정된 key의 값(객체)을 반환한다. 키를 못찾으면 기본값(defaultvalue)으로 지정된 객체를 반환. |
| boolean isEmpty() | HashMap이 비어있는지 알려준다. |
| Set keySet() | HashMap에 저장된 모든 키가 저장된 Set을 반환. |
| Object put(Object key, Object value) | 지정된 키와 값을 HashMap에 저장 |
| void putAll(Map m) | Map에 저장된 모든 요소를 HashMap에 저장 |
| Object remove(Object key) | HashMap에서 지정된 키로 저장된 값(객체)을 제거 |
| Object replace(Object key, Object value) | 지정된 키의 값을 지정된 객체(value)로 대체 |
| boolean replace(Object key, Object oldValue, Object newValue) | 지정된 키와 객체(oldValue)가 모두 일치하는 경우에만 새로운 객체(newValue)로 대체 |
| int size() | HashMap에 저장된 요소의 개수로 반환 |
| Collection values() | HashMap에 저장된 모든 값을 Collection의 형태로 반환 |
▶ 구현 1
id, pwd를 입력받는다.
public class smple {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("myId", "1234");
map.put("asdf", "1111");
map.put("asdf", "1234"); //값이 다른경우 마지막 값으로 저장된다.
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
System.out.println("id와 psw를 입력하세요.");
System.out.print("id : ");
String id = s.nextLine().trim();
System.out.print("password :");
String password = s.nextLine().trim();
System.out.println();
if(!map.containsKey(id)){
System.out.println("입력하신 id는 존재하지 않습니다. 다시 입력하세요.");
continue;
}
if(!(map.get(id)).equals(password)){
System.out.println("비밀번호가 일치하지 않습니다. 다시 입력하세요");
}
else{
System.out.println("id와 비밀번호가 일치합니다.");
break;
}
}
}
}
▶ 구현 2
총점, 평균, 최저 최고점을 구한다.
public class smple {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map= new HashMap();
map.put("김자바", new Integer(90));
map.put("김자바", 100);
map.put("이자바", 100);
map.put("강자바", 80);
map.put("안자바", 90);
Set set = map.entrySet();
Iterator it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)it.next();
System.out.println("이름 : " + e.getKey() + ", 점수 : " + e.getValue());
}
set = map.keySet();
System.out.println("참가자 명단 : " + set);
Collection values = map.values();
it = values.iterator();
int total = 0;
while(it.hasNext()) {
int i = (int) it.next();
total += i;
}
System.out.println("총점 : " + total);
System.out.println("평균 : " + (float) total/set.size());
System.out.println("최고점수 : " + Collections.max(values));
System.out.println("최저점수 : " + Collections.min(values));
}
}
▶ 구현 3
텍스트의 단어 빈도수를 계산한다.
public class ex11_18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] data = {"A", "K", "A", "K", "D", "K", "A", "K", "K", "K", "Z", "D"};
HashMap map = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0; i < data.length; i++){
if(map.containsKey(data[i])) {
int value = (int)map.get(data[i]);
map.put(data[i], value + 1);
}
else{
map.put(data[i], 1);
}
}
Iterator it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)it.next();
int value = (int)e.getValue();
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " : " + printBar('#', value) + " " + value);
}
}
private static Object printBar(char c, int value) {
char[] bar = new char[value];
for(int i = 0; i < bar.length; i++) {
bar[i] = c;
}
return new String(bar);
}
}
▶ 구현 4
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// key와 value를 연결해서 넣어줌
map.put(1, "abc");
map.put(2, "def");
map.put(3, "ksb");
map.put(4, "abc");
map.put(5, "def");
Set<Integer> kSet = map.keySet();
for(Integer n : kSet){
System.out.println(map.get(n));
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
Iterator<Integer> iter = kSet.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
Integer i = iter.next();
System.out.println(i + ":" + map.get(i));
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
// print the data of map
System.out.println(map.get(1));
System.out.println(map.get(2));
System.out.println(map.get(3));
System.out.println("-------------------");
// delete the data of map
map.remove(1);
System.out.println(map.get(1)); //null
System.out.println(map.size()); //2
}
▶ Person Class
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, Person> map = new HashMap<Integer, Person>();
map.put(1, new Person("John", 19));
map.put(2, new Person("Sam", 34));
map.put(3, new Person("K", 27));
map.put(4, new Person("V", 25));
map.put(5, new Person("Owen", 33));
Set<Integer> kSet = map.keySet();
Iterator<Integer> iter = kSet.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Integer i = iter.next();
System.out.println(i + " : " + map.get(i));
}
}
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
// 단순한 정렬이 아닌 기준이 존재하는 정렬을 생성한다.
private String name;
private int age;
Person(){
this("none", 0);
}
Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// getter
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person other) {
// 이름의 글자수 기준, 오름차순
if(this.name.length() > other.name.length()){
return 1;
}
else if(this.name.length() < other.name.length()){
return -1;
}
else{ //같은 경우
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Person[name : " + name + ", age : " + age + "]";
}
}
반응형
'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] Collections Framework - Comparator & Comparable (0) | 2022.07.28 |
|---|---|
| [Java] Collections Framework - Collections method (0) | 2022.07.26 |
| [Java] Collections Framework - Set (0) | 2022.07.26 |
| [Java] Collections Framework - Arrays (0) | 2022.07.24 |
| [Java] Collections Framework - Stack & Queue (0) | 2022.07.21 |
